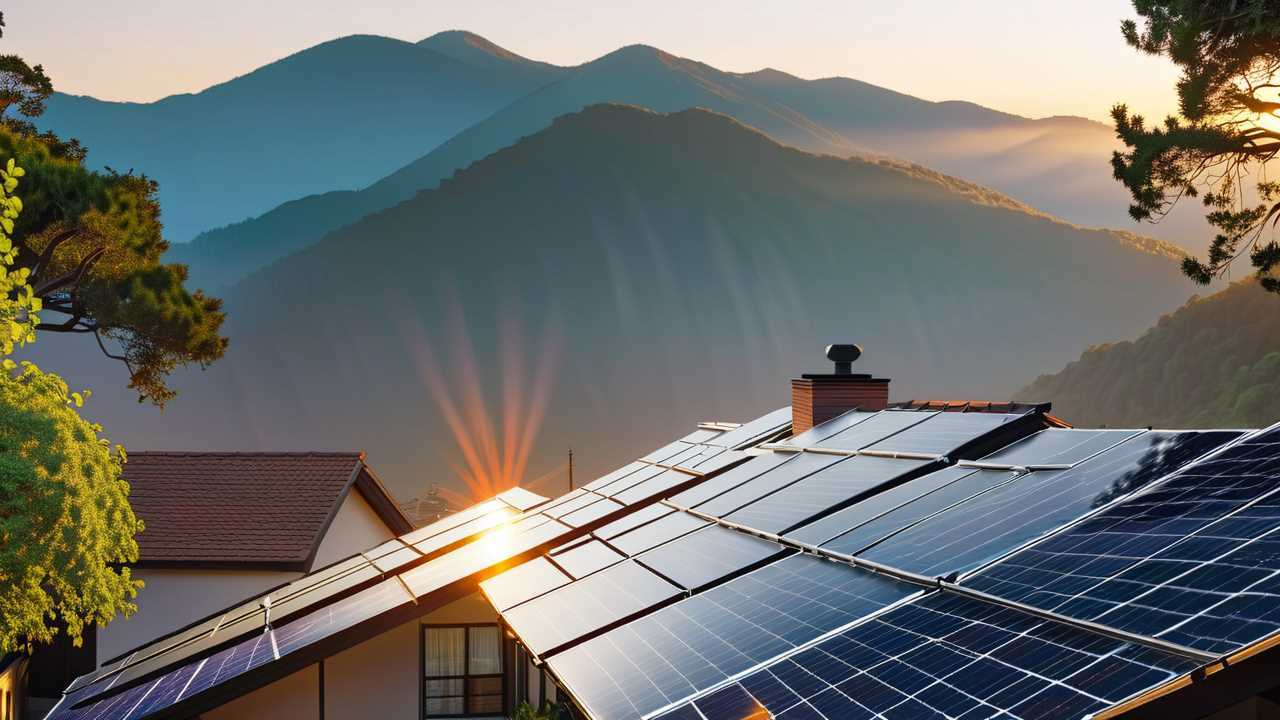

Understanding Solar Energy Basics
Solar energy has become an increasingly popular option for homeowners looking to reduce their energy bills and minimize their carbon footprint. DIY solar power systems allow you to harness the sun's energy and generate electricity for your home or property. To effectively implement a DIY solar power project, it is essential to understand the basic components and principles involved.
Solar Panels: The Heart of Your System
At the core of any solar power system are the solar panels. These panels are made up of photovoltaic (PV) cells that convert sunlight into electricity. When choosing solar panels for your DIY project, consider factors such as efficiency, durability, and compatibility with your specific needs. Monocrystalline and polycrystalline panels are the most common types, each with their own advantages in terms of efficiency and cost-effectiveness.
Inverters: Converting DC to AC Power
Solar panels generate direct current (DC) electricity, but most household appliances and electronics require alternating current (AC) power. This is where inverters come into play. Inverters convert the DC electricity produced by your solar panels into usable AC power. There are two main types of inverters: string inverters and microinverters. String inverters are centralized units that connect multiple solar panels, while microinverters are attached to individual panels, allowing for more precise monitoring and optimization.
Batteries: Storing Energy for Later Use
If you want to store the excess energy generated by your solar panels for use during low-light conditions or power outages, you will need to incorporate batteries into your DIY solar power system. Lead-acid and lithium-ion batteries are the most common options, with lithium-ion batteries offering higher energy density and longer lifespans. When selecting batteries, consider factors such as capacity, depth of discharge, and compatibility with your inverter.
Installation and Mounting: Putting Everything Together
Proper installation is crucial for the performance and longevity of your DIY solar power system. You will need to determine the optimal location and orientation for your solar panels to maximize their exposure to sunlight. Mounting hardware, such as racking systems and roof attachments, will securely hold your panels in place. It is important to follow local building codes and obtain any necessary permits before beginning your installation.
Electrical Connections and Safety
Connecting your solar panels, inverters, and batteries requires careful attention to electrical wiring and safety protocols. Use appropriate gauge wires, connectors, and fuses to ensure a safe and efficient system. Grounding your system properly is also essential to protect against electrical surges and minimize the risk of fire or injury. If you are not confident in your electrical skills, it may be wise to consult with a professional electrician.
Monitoring and Maintenance
Once your DIY solar power system is up and running, regular monitoring and maintenance will help ensure optimal performance and longevity. Many inverters come with built-in monitoring systems that allow you to track your energy production and consumption. Periodically inspecting your panels for damage, cleaning them to remove debris, and checking electrical connections will help keep your system running smoothly.
Expanding Your System Over Time
One of the benefits of a DIY solar power system is the ability to start small and expand as your energy needs grow or your budget allows. By designing your system with future expansion in mind, you can easily add more panels, upgrade your inverter, or increase your battery storage capacity down the line.
Conclusion
Embarking on a DIY solar power project can be a rewarding and cost-effective way to generate clean, renewable energy for your home. By understanding the key components—solar panels, inverters, and batteries—and following best practices for installation, safety, and maintenance, you can successfully harness the power of the sun and reduce your reliance on traditional energy sources. With careful planning and execution, your DIY solar power system will provide reliable, sustainable energy for years to come.
 Family Craft ProjectsHome ImprovementCooking and BakingReuse and RecycleDIY GiftsEco-Friendly ProjectsDIY Home SolutionsSeasonal ActivitiesFun and GamesLearn TogetherPrivacy PolicyTerms And Conditions
Family Craft ProjectsHome ImprovementCooking and BakingReuse and RecycleDIY GiftsEco-Friendly ProjectsDIY Home SolutionsSeasonal ActivitiesFun and GamesLearn TogetherPrivacy PolicyTerms And Conditions
